NAIMA has just released a new course that is available through Hanley Wood University (owned by Zonda). The course, “Resilient Design: Fire Safety, Mineral Wool, and Sustainability,” discusses the construction industry’s vulnerability to natural and manmade hazards that can result in everything from reducing the lifespan of infrastructure, to loss of life and property. Architects, engineers, and construction industry professionals can mitigate these vulnerabilities by having a fuller understanding of resilience as well as the building materials and construction and operational techniques that lead to stronger, more durable buildings.
Details »Insulation Institute Blog
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) last month released the latest version of the Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH) requirements for single-family homes. Version 2 of the ZERH requirements included an update of the thermal envelope insulation levels to those required by the 2021 Residential IECC, whereas the previous version (V1 Rev 8) stipulated 2015 IECC thermal insulation requirements. DOE also highlighted the new tax credits available to builders through the 45L builder energy efficiency tax incentive.
Details »Whew! How did 2022 go so quickly?!
Details »NAIMA recently announced the results of its annual recycled content survey, which reports its members’ use of recycled materials. In 2021, NAIMA members in the U.S. and Canada used more than 3.3 billion pounds of recycled glass and slag in the production of residential, commercial, industrial, and air handling thermal and acoustical insulation.
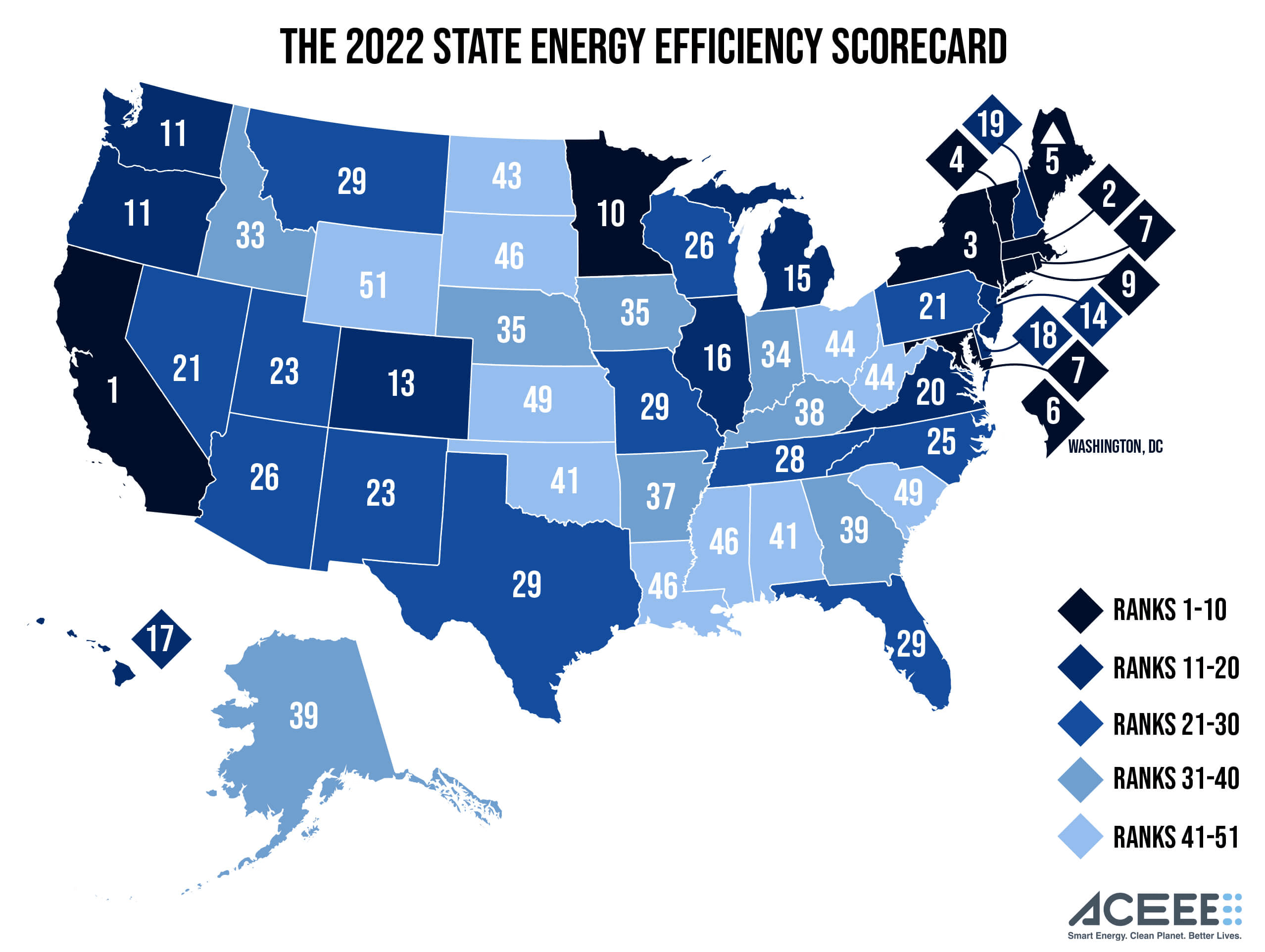
Details »With the high cost of utilities, a federal mandate to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and a renewed push for more energy-efficient buildings, some states have implemented programs and policies that ramp up energy efficiency. In fact, 10 U.S. states are on the leading edge of efficiency because of state policies that prioritize it. Unfortunately, other states are laggards, according to the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy’s (ACEEE) newly released 2022 Energy Efficiency Scorecard.
Details »Building industry members have an opportunity from November 11-13 to learn about Passive House buildings in the U.S. and globally during the International Passive House Open Days. Organized by the International Passive House Association, the event will provide the opportunity for those interested in these highly energy-efficient buildings to learn first-hand how a Passive House build or retrofit works and what it’s like to live and work in a Passive House building.
Details »On Wednesday, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced that $9 billion in funding will be available for states and Tribes from the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) for consumer home energy rebate programs. This funding will allow communities to make homes more energy efficient, upgrade to electric appliances, and make other improvements, such as increasing insulation levels, to reduce energy use.
Details »A new analysis from Ekotrope, the leading provider of home energy rating software, shows U.S. home builders might leave money on the table. Ekotrope software is used to generate energy efficiency insights for one in four U.S. homes. Its analysis concludes that if the homes built this year were slightly more energy efficient, builders could claim more than $160 million in projected tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act’s (IRA) builder tax credit (45L).
Details »The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) ENERGY STAR annual “Rule Your Attic” campaign kicks off on Monday, October 17. The annual campaign encourages homeowners to go into their attic, check their insulation levels, and air seal and insulate if needed. Most homes will need to add insulation as 9 out of 10 U.S. homes are under-insulated.
Details »NAIMA has produced a fact sheet summarizing the energy efficiency tax credits and programs included in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). The IRA offers billions of dollars in incentives for improving building energy efficiency to address climate change, including tax credits and incentives for new construction residential properties, existing home retrofits, and new and existing commercial buildings.
Details »